With the accelerated deployment of the new generation of mobile communication technology 5G in the world, various countries (regions) have gradually separated in the 5G competition. Up to now, the United States, which was originally behind China and South Korea, has made great progress in the past few months. It has not only deployed large-scale 5G services in many cities, but also has a long-term promotion under the guidance of spectrum bidding and policy support. progress.
Compared with the United States, South Korea has also launched 5G network services, but due to insufficient base station density, traffic restrictions on telecom operators’ tariffs, and Nokia’s delayed supply of equipment, South Korea has been frustrated in driving the 5G process.
Back home, it is expected that it will not start to launch 5G commercial services in a few regions until the end of 2019, and because the current three major operators, namely China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, are not half of the original budget in 5G related investment. In addition, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has only issued temporary operation licenses for some cities. The overall 5G progress in China has slowed down, mainly relying on Huawei’s advantages in 5G equipment and smart phones to maintain its leading position in the world.
According to a survey conducted by AnalysisMason, commissioned by CTIA of the US Mobile Communications and Network Association, the United States has made significant progress in the 5G competition recently thanks to policy making, government promotion, and active investment in the industry. In the process of advancing 5G services, US telecom operators have adopted a model of mutual integration with the US communication network reform, which is conducive to the deployment and construction of mobile infrastructure.
In the following, it is worthwhile to review the fierce standards debate in the global communications industry since the 2G era.
(One)
Launched in the early 1990s, 2G communication technology is a voice channel technology that supports line switching. It mainly calls and transmits text messages through voice channels.
At that time, it was divided into two major camps: the GSM, a global mobile communication system introduced by Europe in 1990, and the CDMA technology promoted by Qualcomm. In addition, the personal digital mobile system PDC launched in Japan is basically not competitive in the market.
Compared with GSM, CDMA has the advantages of 10 times larger system capacity, better call quality and higher connection rate on the technical level. It was recognized as an industry standard in 1993, which laid the foundation for Qualcomm to become a giant in the field of mobile communications. . Due to the first-mover advantage of GSM in Europe, international roaming standards have been established in just a few years, and GSM base stations are widely deployed around the world; CDMA has limited construction of base stations, and the number of mobile phone devices supporting CDMA is very limited. Therefore, GSM basically won the victory in the 2G era.
(two)
The 3G mobile communication technology 3G evolved on the basis of 2G. The 3G UMTS system supports packet switching, and the Internet speed is fast. It also supports 2G. Therefore, the voice channel of the GSM system can still be used to make calls or text messages. carry out.
Since the communication industry is an important national strategic industry, the competition between communication standards is a comprehensive struggle between countries and alliances. Everyone wants to grasp the dominant position of the industry and avoid paying high patent fees to each other. In order to prevent Qualcomm from charging high licensing fees by CDMA, countries such as Europe and Japan that have implemented the GSM standard have jointly established a 3GPP organization to develop global third-generation communication standards, and carefully reference CDMA technology to avoid Qualcomm patents. Finally, WCDMA was developed. However, Qualcomm also found South Korea to form 3GPP2, which competes with 3GPP and has developed the CDMA2000 standard.
In order to strive for a favorable situation for themselves, after many private communication, negotiation, wrestling and compromise, in May 2000, the International Telecommunication Union ITU finally formulated three 3G international telecommunication standards, namely the US-led CDMA2000, which was promoted by Europe. WCDMA, as well as China-led TD-SCDMA, are all based on CDMA technology.
Although Qualcomm did not succeed in the 2G era, Qualcomm has accumulated a strong strength for itself through continuous research and development and accumulation of patents. Since the three major standards are based on the basic patented technology of CDMA, neither equipment suppliers, telecom operators, or handcuff manufacturers can avoid paying considerable patent license fees to Qualcomm.
In fact, in the early days, the market did not have much expectations for 3G, especially before the widespread popularity of killer applications. At best, communication was smoother and the sound quality was better. Qualcomm did not make much money.
In order to stay in the leading position in the industry, major European countries began issuing 3G licenses and spectrum bidding as early as 2000. The telecom operators were bidding for big money at the time, and the goal was to earn back the cost through 3G non-voice revenue. However, the problem was that there was not a large demand for mobile applications in the market at the time, which caused many operators to be heavily in debt. Some even gave up the 3G licenses directly. The overall European telecommunications business was badly hurt. After 4 or 5 years, it gradually recovered. Building a 3G network.
Although the United States, which lags behind Europe and did not issue 3G licenses until 2004, has been delayed from launching 3G networks. The most important thing is that in 2007, Apple released the first iPhone smartphone, which finally brought a revolutionary change to the mobile communication industry. The advent of Apple’s iPhone has made mobile Internet meaningful, and it has successfully boosted the scale of 3G users, and it has also made telecom operators profitable.
(three)
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers introduced Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technology in 2003 and introduced a modified version of 802.11g to increase the transmission speed from the original 11Mbps to 54Mbps. Plus multi-input and multi-output MIMO technology not only improves the spectrum. Efficiency, which greatly increases system throughput and transmission distance, makes Wi-Fi the mainstream technology for wireless regional networks.
Because of the optimistic view on Wi-Fi technology, the IT giants led by Intel in the United States jointly announced the development of the 802.16 standard in 2005 to conduct interoperability testing of mobile terminal devices and network devices. The standard is WiMAx. WiMAx is an enhanced version of Wi-Fi, and WiMAx can theoretically transmit up to 50 kilometers at a higher rate.
3GPP also saw the advantages of OFDM technology, but at the same time did not want the United States to lead the standard. So in 2009, the long-term evolution technology LTE was proposed as the next-generation technology standard, and then an upgraded version of LTE-Advanced was proposed in 2011. 4G technical standards, ready to phase out WCDMA.
Intel, Motorola, IBM and other major US companies that have invested nearly $1 billion in WiMAx projects obviously do not want other technical standards to break their plans, so they actively join the telecoms to join, and Intel even claims that the price of WiMAX chips will be higher than Traditional 3G chips are 10 times cheaper.
The United States has given strong support to the WiMAx camp and even pressured the International Telecommunications Union to include WiMAx as the fourth 3G international telecommunications standard and distribute it to the global spectrum.
The United States chose to stand with the European camp. As a result, among the major communications equipment suppliers in the world, the United States only Lucent (later acquired by Alcatel in France), Motorola, and Nortel Canada, still far less powerful than Ericsson. , Alcatel, Siemens’ European camp, plus China’s Huawei and ZTE.
Moreover, the three major international telecommunications standards are based on CDMA technology development, and Qualcomm does not want to develop WiMAx to compete with its own patents. After the failure to negotiate with the WiMAx alliance, Qualcomm decided that all chips did not support WiMAx; at the time, Intel did not foresee the rise of smartphones, and did not focus on the development of hand-held chips.
As a result, the WiMAx camp has fallen apart without equipment supply, hand-held chips, and a complete and mature industry chain. Intel, which led the push, had to announce the withdrawal and dissolution of the WiMAx business unit in July 2010. Asian countries including Malaysia, South Korea, the Philippines and other WiMAx that had embraced WiMAx had to turn to LTE. Nortel, which was fully committed to WiMAx, declared bankruptcy.
The LTE camp includes the world’s major mobile phone and telecom equipment manufacturers. Once the relevant specifications are formulated, it will inevitably drive all telecom operators to follow up. Therefore, LTE has not only become the standard of 4G mobile communication technology 4G, but also the WiMAx.
(four)
4G LTE/LTE-A system supports packet switching and supports 2G and 3G. Therefore, when the mobile phone cannot find the LTE base station, it still uses the UMTS base station to access the Internet, and can still use the voice channel of the GSM system when making a call or sending a text message. carry out.
On January 18, 2012, the International Telecommunication Union officially reviewed and adopted the LTE-A WirelessMANAdvanced (802.16m) technical specification as the IMT-Advanced international standard. The download rate of 4G network can reach 100Mbps to 150Mbps, which is more than 20 times faster than 3G; the upload rate can reach 20Mbsps to 40Mbps.
(Fives)
Now, as we have become accustomed to the services and applications brought by 4G speed and capacity, as 5G launches globally, it is expected to bring new services and applications, including autonomous vehicles, better AR. Innovative applications such as /VR experience, smart factories and the Internet of Things, these innovative applications require ultra-high-speed data transmission and ultra-low latency.
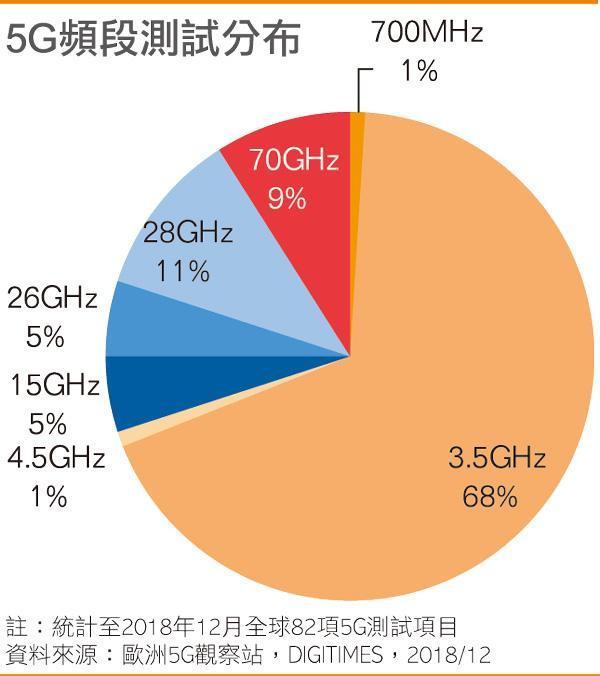
First-class enterprises do standards, second-rate enterprises do services, and third-rate enterprises do products. Whether it is the international standard organization of mobile communication technology or other industries, in the process of standard setting, enterprises hope that their technology can be accepted by the standards development organization and become the industry standard, and then the cost can be reduced in the patent cross-licensing. Therefore, the number of standard patents can be used to measure the industrial strength and competitiveness of enterprises and even the country. Those who are dominant in the number of standard patents have a greater voice in the formulation of industrial standards.